Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet Metal Fabrication Services
Sheet Metal Fabrication Services: Sheet metal fabrication involves the process of cutting, bending, and assembling metal sheets into custom parts or products. These services are used to create components for various industries, including automotive, construction, aerospace, and electronics. Techniques such as laser cutting, punching, welding, and bending ensure precision and high-quality results for both small and large-scale production. Sheet metal fabrication is essential for creating durable, lightweight, and cost-effective parts with complex shapes and designs.
Sheet Metal Services
Sheet Cutting Services
Sheet cutting services involve the precise cutting of metal, plastic, or other materials into custom sizes and shapes based on specific requirements. These services utilize advanced techniques such as laser cutting, waterjet cutting, and shear cutting to achieve high precision and clean edges. Sheet cutting is commonly used in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and automotive, providing tailored solutions for producing components, panels, and various other products quickly and efficiently.

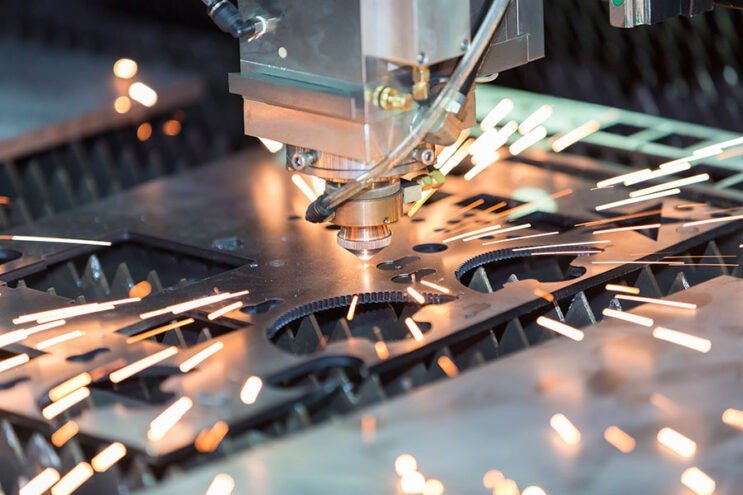
Laser Cutting Service
Laser Cutting Service: Laser cutting is a precise and efficient process that uses a focused laser beam to cut, engrave, or etch various materials, including metal, wood, acrylic, and plastic. This service offers high accuracy, intricate detailing, and smooth edges, making it ideal for complex designs and prototypes. Laser cutting is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, signage, and manufacturing, providing fast turnaround times and the ability to work with a variety of material thicknesses. It is especially valued for its clean cuts and minimal material wastage.
Waterjet Cutting Service
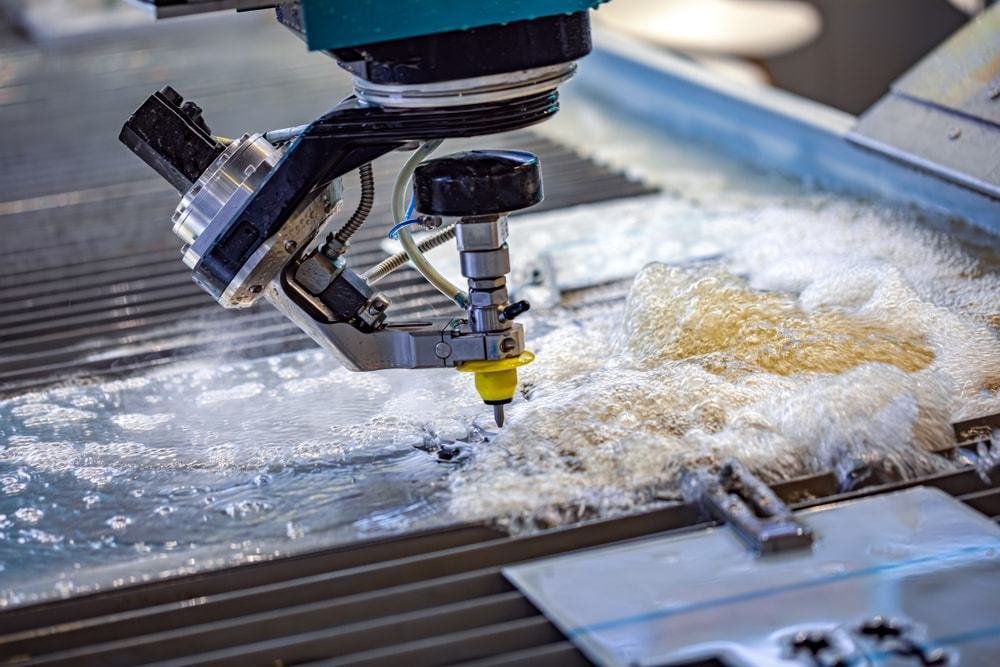
Waterjet Cutting Service: Waterjet cutting is a precision cutting process that uses a high-pressure stream of water, often mixed with an abrasive substance, to cut through a wide range of materials, including metal, stone, glass, and ceramics. This service offers clean, precise cuts without generating heat, which prevents material warping or changes in structure. Waterjet cutting is ideal for intricate designs, thick materials, and complex shapes. It is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, architecture, and manufacturing for its versatility, accuracy, and ability to cut materials that are difficult to machine with traditional methods.

Sheet Metal Fabrication Capabilities
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
|
Blank Size |
5’ x 10’ (1.52 m x 3.05 m). We accommodate larger part volumes upon request. |
|
Standard Lead Time |
3 business days |
|
Sheet Thickness |
0.024” – 0.250” typical. We accommodate thicker or thinner gauges upon request. |
|
General Tolerances |
See our Sheet Metal manufacturing standards for details on general tolerances. |
|
Braking (Hydraulic) |
14′ length |
|
Braking (Magnetic) |
6 tons of magnetic pull across the entire beam, 5/8″ minimum reverse bend |
|
Punching |
2″ diameter hole capacity, or larger upon request |
|
Welding |
Welded edges and seams, weldments, and assemblies |
What is Sheet Metal Forming?
Sheet Metal Forming is a manufacturing process that involves shaping and manipulating flat sheets of metal into desired forms through various mechanical processes. This is achieved by applying forces to the sheet metal to change its shape without adding or removing material. Sheet stock is initially procured in a flat state and then cut and formed into its final shape through a series of progressive steps. For a typical sheet metal project, the first step involves sheet cutting, where tools like a shear, laser, waterjet or punch press are used to create internal holes and edge features of the part. This stage is commonly referred to as blanking, where the basic shape or blank of the part is created before further forming processes are applied.
How Sheet Metal Fabrication Works?
Design and CAD Modeling
The process begins with creating a design for the part, typically using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This model includes precise specifications for the part’s dimensions, features, and material requirements.
Material Selection
The appropriate sheet metal material (such as steel, aluminum, copper, or brass) is selected based on the part’s intended use, including factors like strength, weight, and corrosion resistance.
Cutting (Blanking)
The sheet metal is cut to the required size using methods like shearing, laser cutting, waterjet cutting, plasma cutting, or punching. This initial step, also called blanking, creates the basic shape or blank that will be further processed.
Bending/Forming
The cut sheet metal is then bent into the desired shape using a press brake or other bending machines. This process can create various angles and curves, depending on the part’s design. Other forming techniques, like deep drawing or stretch forming, may also be used to create more complex shapes.
Hole Punching and Stamping
For parts requiring holes, slots, or other features, a punch press or stamping process is employed. Stamping uses a die and punch to create holes or shapes in the metal, while punching involves a similar method to cut out parts from the sheet.
Welding and Joining
If multiple parts are needed to be assembled, welding, riveting, or fastening techniques are used to join the sheet metal components together. Welding methods like TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas), MIG (Metal Inert Gas), or spot welding are commonly employed.
Finishing
After the part is fabricated, finishing processes such as deburring, sanding, powder coating, painting, or anodizing may be applied to improve the surface finish and durability of the product. These steps also enhance the part’s appearance, providing a smooth or textured surface.
Inspection and Quality Control
Throughout the fabrication process, quality checks and inspections are conducted to ensure that the parts meet design specifications, tolerances, and quality standards.
Final Assembly and Packaging
If needed, fabricated parts are assembled into larger products or systems. The final parts are then packaged and shipped to the customer.
Applications of Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet Metal Materials
Aluminum
- Aluminum 1100-H14
- Aluminum 5052-H32
- Aluminum 6061
Copper
- Copper 101
- Copper C110
- Copper C110, H02
- Copper 260 (Brass)
Bronze
- Bronze 220
- Bronze 510
Stainless Steel
- Stainless steel 301
- Stainless steel 304
- Stainless Steel 304 #4 brushed
- Stainless Steel 304, #8 mirror polish
- Stainless steel 316/316L
- Stainless Steel 316, #4 brushed
Steel
- Steel 1018 (Low Carbon)
- Steel 1045 (Hot Rolled)
- Steel A569/ASTM A1011 (Hot Rolled)
- AZ55 Galvalume
- A653 Galvanized
- 1095 Spring Steel
- Steel A36
- Steel A36, pickled and oiled
- Steel A366/1008
Nickel Alloys
- Inconel 625
- Nickel Alloy 200
- Nickel Alloy 400
Titanium
- Titanium (Grade 2)
- Titanium 6AI-4V (Grade 5)
Sheet Metal Design Guidelines
| Feature | Description (MT = Material Thickness) |
|---|---|
|
Minimum Bend |
1X MT |
|
Minimum Hole to Edge Distance |
2X MT |
|
Minimum Hole to Hole Distance |
6X MT |
|
Minimum Bend Edge to Hole Distance |
6X MT |
|
Minimum Feature to Countersink Distance |
8X MT |
|
Minimum Countersink Depth |
0.6X MT |
|
Relief Cuts |
1X MT |
|
Corner Fillets |
0.5X MT |
Why Choose Avinyaworks for Sheet Metal Fabrication Services?
Endless Options
Choose from millions of possible combinations of materials, finishes, tolerances, markings, and certifications for your order.
Easy to Use
Get your parts delivered right to your door without the hassle of sourcing, project management, logistics, or shipping.

