Sheet Cutting
What is Sheet Cutting?
Sheet Cutting is the process of cutting flat sheets of metal, plastic, or other materials into specific shapes and sizes using various cutting techniques. This process is an essential first step in sheet metal fabrication, where precise cuts are made to prepare the material for further forming, bending,
- Metals
- Plastics
- Wood
- Composites
- Foams
- Rubber & Gaskets
Cutting Services
Laser Cutting Service
Laser Cutting Service: Laser cutting is a precise and efficient process that uses a focused laser beam to cut, engrave, or etch various materials, including metal, wood, acrylic, and plastic. This service offers high accuracy, intricate detailing, and smooth edges, making it ideal for complex designs and prototypes. Laser cutting is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, signage, and manufacturing, providing fast turnaround times and the ability to work with a variety of material thicknesses. It is especially valued for its clean cuts and minimal material wastage.
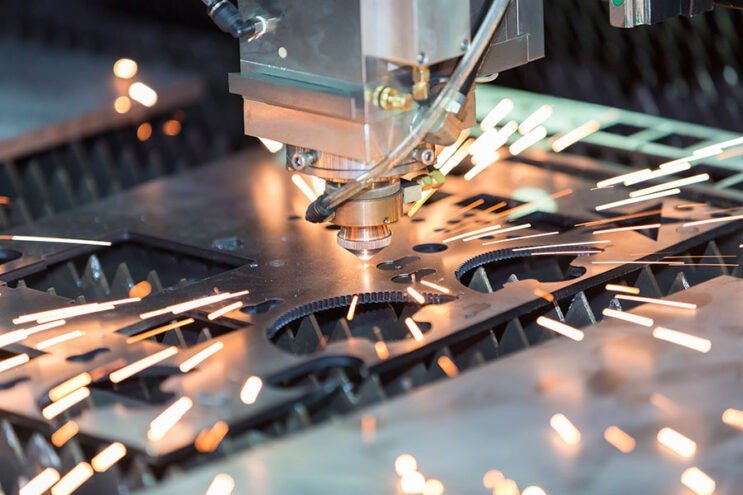
Waterjet Cutting Service
Waterjet Cutting Service: Waterjet cutting is a precision cutting process that uses a high-pressure stream of water, often mixed with an abrasive substance, to cut through a wide range of materials, including metal, stone, glass, and ceramics. This service offers clean, precise cuts without generating heat, which prevents material warping or changes in structure. Waterjet cutting is ideal for intricate designs, thick materials, and complex shapes. It is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, architecture, and manufacturing for its versatility, accuracy, and ability to cut materials that are difficult to machine with traditional methods.
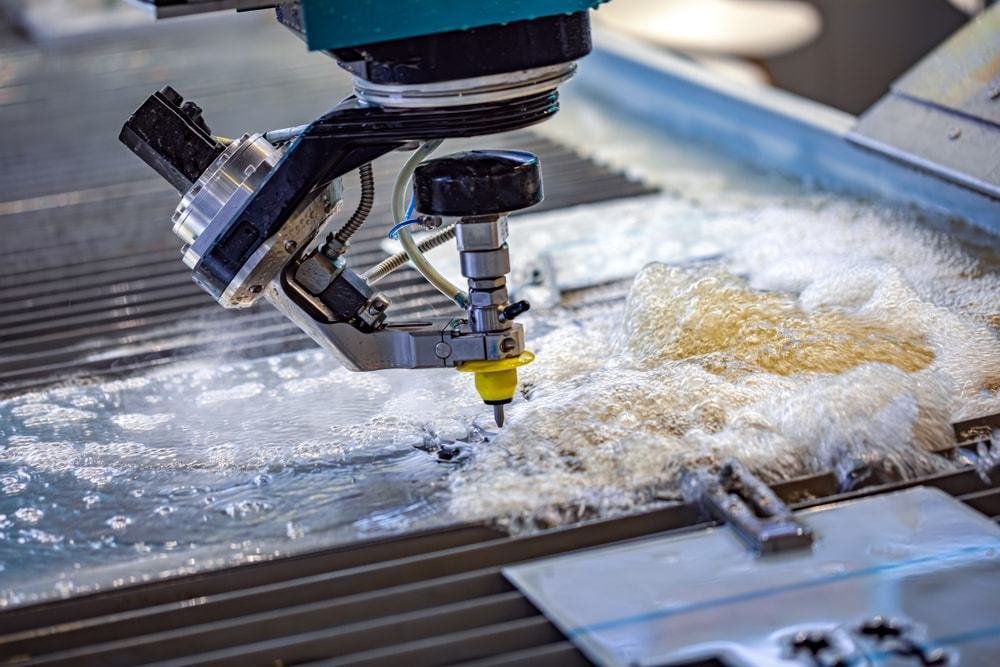

Sheet Cutting Sizes and Tolerances
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
|
Blank Size |
Avinyaworks has access to platforms up to 10’ x 20’ for laser cutting and waterjet cutting. However, many sheet stock sizes commonly cap out at 48” x 96” (4’ x 8’) or smaller. |
|
Standard Lead Time |
3 business days |
|
Sheet Thickness |
0.020″ up to beyond 1.00″ depending on materials. Thinner or thicker stock may be possible through manual quoting. |
|
General Tolerances |
For full details on tolerances offered by Avinyaworks sheet cutting service, including edge to edge tolerance and taper, please consult our manufacturing standards. |
How are Laser Cutting and Waterjet Cutting Different?
Laser Cutting uses a concentrated beam of light to melt, burn, or vaporize material along the cutting path. This process is highly efficient for cutting thin materials, especially metals, plastics, and wood. Laser cutting provides precise, clean cuts with smooth edges, often requiring minimal post-processing. However, the intense heat generated during the cutting process can cause heat-affected zones (HAZ), which can lead to material distortion, especially with thicker materials. Laser cutting is faster than waterjet cutting, making it ideal for high-volume production of thinner parts.
Waterjet Cutting, on the other hand, employs a high-pressure stream of water, sometimes combined with abrasive materials, to cut through a wide range of materials. Unlike laser cutting, waterjet cutting is a cold process, meaning it does not generate heat and therefore avoids heat-affected zones, preserving the material’s integrity. It is capable of cutting much thicker materials than laser cutting and is particularly effective for heat-sensitive materials like ceramics, glass, and certain metals. However, waterjet cutting tends to be slower than laser cutting, especially when working with thin materials. Additionally, the cutting edges can be slightly rougher and may require more post-processing.
How Sheet Cutting Works?
Material Selection
The first step is choosing the material to be cut. Common materials include metals (steel, aluminum, copper), plastics (acrylic, polycarbonate), and composites. The material’s thickness and properties influence the choice of cutting method.
Design & Measurements
A design or blueprint of the part is created, often in CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. Precise measurements and cutting instructions are included to ensure accuracy. The design is then transferred to a machine-readable format, such as DXF, DWG, or PDF files.
Cutting Method Selection
Depending on the material and thickness, one of several cutting methods will be chosen:
- Shearing: A mechanical process that uses two blades to cut the material in a straight line. Ideal for quick, straight cuts.
- Laser Cutting: Uses a high-powered laser beam to melt, burn, or vaporize material. This is suited for precise cuts in thin metals, plastics, and some non-metals.
- Waterjet Cutting: Involves using a high-pressure stream of water, sometimes mixed with abrasives, to cut through a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and stone.
- Plasma Cutting: Uses a plasma torch to cut through conductive materials like steel and aluminum. This method is faster than laser cutting for thicker materials.
- Punching: Uses a punch press to create holes or shapes in sheet material, suitable for repetitive cutting.
Cutting the Material
The selected cutting method is then employed to cut the material according to the design. In laser, waterjet, and plasma cutting, the machine follows the contours of the design with high precision. For shearing and punching, the material is manually or automatically fed into the machine, which executes the cuts.
Quality Control
After cutting, the parts are inspected to ensure they meet the required specifications. This may involve measuring dimensions, checking for burrs or defects, and ensuring the cuts are clean and accurate.
Post-Processing (Optional)
Depending on the cutting method and material, additional post-processing may be required to refine the edges or remove excess material. For example, laser-cut parts may require deburring to remove sharp edges, while waterjet-cut parts might need drying.
Sheet Cutting Materials
Aluminum Alloy
Aluminum 6061 T6, Aluminum 2024-T3, Aluminum 5052 H32, Aluminum 7075 T6, Aluminum MIC6
Brass and Bronze Alloy
Brass 260, Brass 353 H02, Brass 464 H01, Bearing Bronze 932 M07, Bronze 220 H02, Bronze 510 H08 (spring) Silicon Bronze 655
Copper Alloy
Copper 101, Copper 110
Mechanical Plastic
ABS, Acetal (POM, Delrin), PETG, PC, PP, PTFE, PVC, UHMW
Acrylic
Clear and Colored Acrylic (Plexiglass)
Foam
EVA Foam, Polyurethane Foam (PU), Silicone Foam
Steel
Steel 1075, 1095, 4130, AR500, AR500, Corten A588, 1045 HR, A1011 HR, 1008, 1018, 4140, A36, A366, A572, A653, G90, Tool Steel D1, O1
Stainless Steel
Stainless 17-4 PH, 17-7, 301, 304, 316, 410, 430, 440C, CPM 154, S30V
Other Metal Alloys
Titanium Grade 2 and 5, Nickel Alloy
Wood
Cherry, Hardboard, MDF, Poplar, Red Oak, Wood Laminate (Plywood)
Carbon Fiber and Other Composites
Carbon Fiber, Garolite G-10, Garolite G-11, Garolite LE (Phenolic)
Rubber and Gasketing
Buna-N Rubber Blends, EPDM, Silicone Rubber, Paper Fiber, PTFE
Why Choose Avinyaworks for Sheet Cutting Services?
Endless Options
Choose from millions of possible combinations of materials, finishes, tolerances, markings, and certifications for your order.
Easy to Use
Get your parts delivered right to your door without the hassle of sourcing, project management, logistics, or shipping.
Quality Assurance
Our quality check includes visual inspection, dimensional verification, functionality testing (if applicable), and a review of surface finish.

