Injection Molding Service
What Is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is the most cost-effective method for producing plastic parts at scale. The process involves injecting molten plastic into a mold tool, where it cools and solidifies to form the part. Once cooled, the part is ejected from the mold, and the process is repeated rapidly—hundreds or thousands of times—allowing for high-volume production. This efficiency helps amortize the upfront cost of the mold, significantly reducing the per-unit cost, often to just a few dollars or even less, depending on the complexity and volume.
Since the same mold tool is used for each part, injection molding ensures consistent quality across all units, with minimal variation between parts. The process also offers a wide range of material options, including various types of plastics, colors, cosmetics, polishes, and surface textures, giving you greater flexibility compared to methods like CNC machining or even 3D printing. Whether you need high strength, flexibility, or specific aesthetic features, injection molding can deliver the required results with precision and repeatability.
Injection Molding Services
Prototype Molding
Prototype molding is a crucial process used to create a small number of functional parts quickly and cost-effectively for testing, validation, or design iteration. It allows designers, engineers, and manufacturers to produce prototypes that simulate the final product without the high upfront costs associated with full-scale production tooling. Prototype molding is typically used in the early stages of product development to verify design concepts, check fit and form, and perform functional testing.
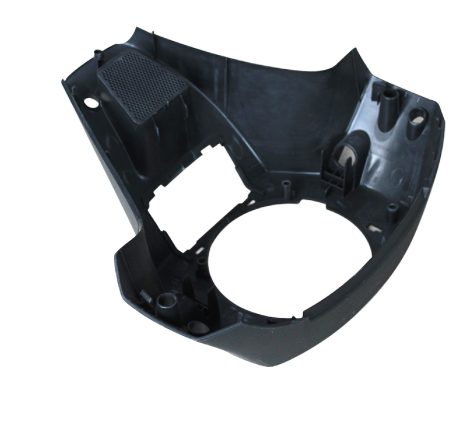

Overmolding
Overmolding is a manufacturing process where one material is molded over a previously molded part to create a multi-material component. It’s often used to combine two or more materials to achieve specific functional or aesthetic properties in a single part. Overmolding allows for the integration of features like soft-touch grips, insulation, sealing, or improved aesthetics without the need for additional assembly processes.

Insert Molding
Insert Molding is a specialized form of injection molding where pre-formed components (called inserts) are placed into a mold cavity and then overmolded with plastic or other materials to form a single, integrated part. The insert can be made of materials such as metal, plastic, ceramics, or composites. The result is a part that combines the benefits of both materials—such as the strength of metal with the flexibility or lightweight properties of plastic—into a single, unified component.
Injection Molding Capabilities
| Service | Details |
|---|---|
|
Lead Time |
Starts at 5 business days, including fast quote responses with design-for-manufacturing (DFM) feedback |
|
Production Options |
Domestic and international |
|
Materials |
Most plastics, including custom sourcing and matching; see materials list below |
|
Machines Available |
Single, multi-cavity, and family molds; 50 to 3,700+ press tonnage; automated side actions or hand-loaded cores. |
|
Inspection and Certification Options |
Includes FAI and PPAP. ISO 9001, AS9100, ISO 13485, UL, ITAR, and ISO 7 and 8 Medical Clean Room molding. |
|
Tool Ownership |
Customer-owned with mold maintenance |
|
Mold Cavity Tolerances |
+/- 0.005″ when machining the mold and an additional +/- 0.002″ per inch when calculating for shrink rate |
|
Part to Part Repeatability |
+/- 0.004″ or less |
|
Critical Feature Tolerances |
Tighter tolerances can be requested and may increase the cost of tooling because of additional sampling and grooming. We will mill to a steel-safe condition on critical features. |
|
Available Mold Types |
Steel and aluminum; Production grades range from Class 105, a prototype mold, to Class 101, an extremely high production mold. We typically produces Class 104, 103, and 102 tools. |
How Custom Plastic Injection Molding Works?
Custom plastic injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce plastic parts in high volumes with high precision. It involves injecting molten plastic material into a custom-designed mold to form the desired shape and features of the part. The mold is specifically created to match the exact requirements of the part, including its size, shape, and any additional features (like holes, textures, or logos). This process is widely used across industries such as automotive, electronics, consumer goods, medical devices, and packaging, due to its ability to produce complex parts quickly and at scale.
Custom Plastic Injection Molding Materials
Rigid Plastic Materials:
ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene)
High-strength general-purpose engineering plastic, used for many commercial products.
ASA (acrylonitrile styrene acrylate)
A material very similar to ABS with higher resistance to fading and better suited for outdoor use.
CA (cellulose acetate)
Typically used in eyeglasses and film, CA is a flexible clear material that can be used in food contact.
HDPE (high-density polyethylene)
xcellent strength-to-weight ratio and chemical resistance. It is often used for fuel tanks, connector insulators, and food containers. HDPE is also used in outdoor equipment like playgrounds.
LCP (liquid crystal polymer)
LCP has mechanics even at elevated temperatures as well as low dielectric constants. This material provides exceptional features for micromolding and thin walled components. LCP is popular for electrical connectors and interconnects as well as medical devices.
LDPE (low-density polyethylene)
A flexible and tough material with lower density versus HDPE. LDPE does not react to acids, bases, or alcohols. Useful for trays, snap lids, and general-purpose containers.
PA 6 (polyamide 6, nylon 6)
Offers increased mechanical strength, rigidity, good stability under heat, and/or chemical resistance.
PA 6/6 (polyamide 6/6, nylon 6/6)
Offers increased mechanical strength, rigidity, good stability under heat, and/or chemical resistance.
PARA (polyarylamide)
Often combined with infills such as glass or mineral fibers, PARA creates rigid parts with low creep and a slower rate of water absorption than nylon (PA). PARA is excellent for structural components in handheld and medical electronics.
PBT (polybutylene terephthalate, Valox)
A common electronic insulator with a polyester base. Highly used in automotive as a longer-wear alternative to nylon.
PBT-PET (polybutylene terephthalate-polyethylene terephthalate)
A compounded blend of PBT and PET.
PVC (polyvinyl chloride (Shore D))
A rigid, general-use plastic that is common in plumbing, non-food packaging, and trimming.
PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride, Kynar)
A chemically inert, high-temperature material. Due to its low friction, PVDF is used in plumbing parts, bearings, chemical handling, electrical wire insulation, and tubing.
TPO (thermoplastic polyolefin)
A flexible plastic with good chemical resistance but lower temperature resistance compared to PP.
Elastomer and Rubber Molded Materials:
EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber (Viton))
One of the highest performing rubber elastomers with high heat resistance, chemical resistance, and moisture sealing properties. EPDM is commonly found in automotive seals, gaskets, O-rings, and electrical insulators.
PEBA (polyether block amide)
A soft, flexible, plastic or elastomer used for medical devices such as catheters. PEBA foams are used for padding, shoe insoles, and sports equipment. PEBA is resistant to moisture and UV exposure.
PVC (polyvinyl chloride (Shore A))
A soft rubber-like, general use elastomer, that is common in outdoor products, protective films, and mats. Shore A rubber-like PVC requires plasticizers to improve its flexibility from its typical rigid state. PVC is flame retardant due to self-extinguishing properties.
TPE (thermoplastic elastomer)
A broad class of elastomers that behave like a thermoset with high flex and elasticity but process like a thermoplastic through molding. TPE is an umbrella term for many unique elastomer classes.
TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane (Shore A))
A tough, highly abrasion-resistant elastomer that bridges the gap between rubbers and plastics. TPUs can be formulated to be rigid or elastomeric. TPU exhibits a high flex before break and is ideal for flexible tires, skateboard wheels, and weatherproof gaskets.
TPV (thermoplastics elastomer, vulcanized rubber (Santoprene))
An excellent elastomer with high versatility due to temperature resistance, compression, and elasticity.
LSR (liquid silicone rubber)
Silicones are versatile rubber materials offering food and biocompatibility, extreme heat resistance, and excellent flexibility. LSR is used for medical devices, automotive, aerospace, and consumer products. Liquid silicone rubber molding is a specialized process different from traditional injection molding.
Injection Moldings Design Guidelines
| Feature | Tip |
|---|---|
|
Undercuts |
Reduce undercuts, which will increase the complexity and cost of the tool ejection mechanisms, by adding in pass-thru coring. |
|
Wall Thickness |
Prevent wall sink and voids by maintaining an even wall thickness. Thinner walls reduce cycle time and reduce costs. |
|
Drafts |
Ensure parts are designed with a minimum draft angle of 0.5°, or up to 5°, for faces with medium textures. |
|
Ribs/Gussets |
Ribs should be 40-60% the thickness of outer walls and should still maintain draft. |
|
Bosses |
Bosses should be designed at a depth of 30% the wall thickness and with a 30% edge groove. Attach them to side walls or ribs for structural integrity. |
Why Choose Avinyaworks for Injection Molding Services?
Endless Options
Choose from millions of possible combinations of materials, finishes, tolerances, markings, and certifications for your order.
Easy to Use
Get your parts delivered right to your door without the hassle of sourcing, project management, logistics, or shipping.
Quality Assurance
Our quality check includes visual inspection, dimensional verification, functionality testing (if applicable), and a review of surface finish.

